Dos and Don’ts of Behavior Reflection
Do you struggle with helping students process their behaviors and learn to make better choices? Are your time-outs ineffective? Are your students repeating the same negative behaviors? Having strategies for effective behavior reflection is critical to creating a positive learning environment (and staying sane).
Dos
- Choose the appropriate behavior reflection form based on your students’ levels (reading, developmental, age, etc.)
- Present this tool to the student in a 1:1 setting after their behavior has deescalated and they are ready to reflect
- Provide supports in completion (e.g., teacher prompting, student can dictate to adult)
- Select, model and practice appropriate replacement behaviors for the future
- Guide student to write an apology letter to help them realize how their behavior affects others
- Copy and send home for parental signature; save original in student file for behavior documentation and data collection
Don’ts
- Use for every minor behavior infraction; instead focus on target behavior(s) and/or moderate to severe issues
- Present and discuss in front of whole class
- Forget to review and discuss the behavior reflection and appropriate replacement behaviors with student
- Overlook positive behaviors and attempts to make better choices
Two versions of the Think Sheet are included, as well as a template for an apology letter.
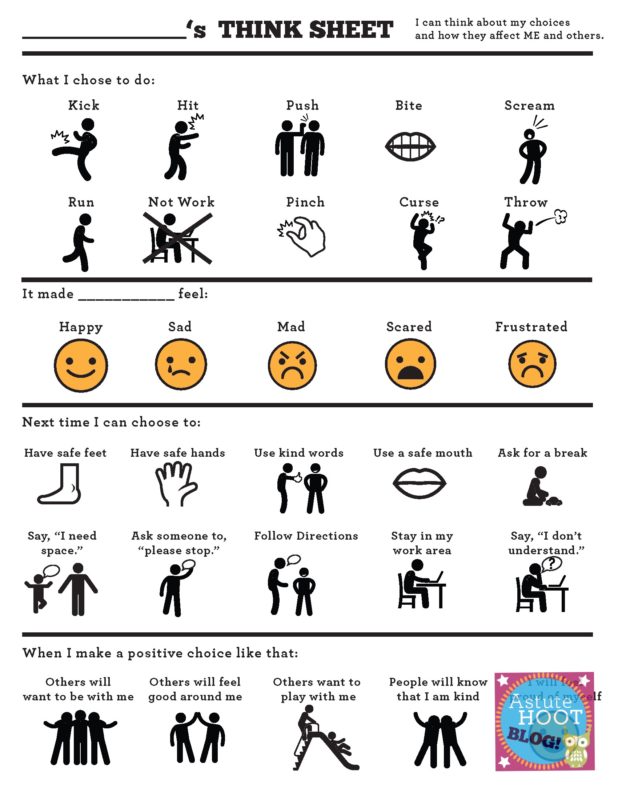
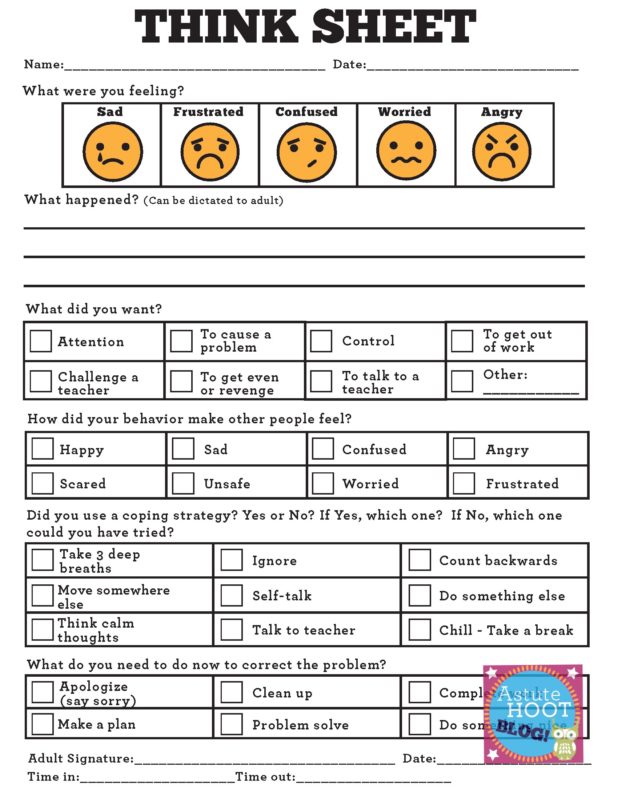
Download the Think Sheet and other helpful behaviors tools here!